A comprehensive and integrated database could provide coherent information to users and advance either scientific or practical progresses. LettuceGDB (www.LettuceGDB.com), which integrates the public datasets and all the lettuce data generated by our group. This database includes multiple types of data, such as multi-omics data including genome, re-sequencing, transcriptome, miRNAome, epigenome, metabolome, and integrates a wealth of germplasm resource with abundant phenotypic data collected from manually records and high-throughput phenomic platforms. In order to enable users to access these data conveniently, we have designed easy-to-use access functions/interfaces and multiple tools including a data download center. Finally, we also developed a communication platform, where we systematically summarize the current research progress on different aspects of lettuce. Taken together, we believe that LettuceGDB can serve the entire research community and assist the both scientific research and breeding practice of lettuce.
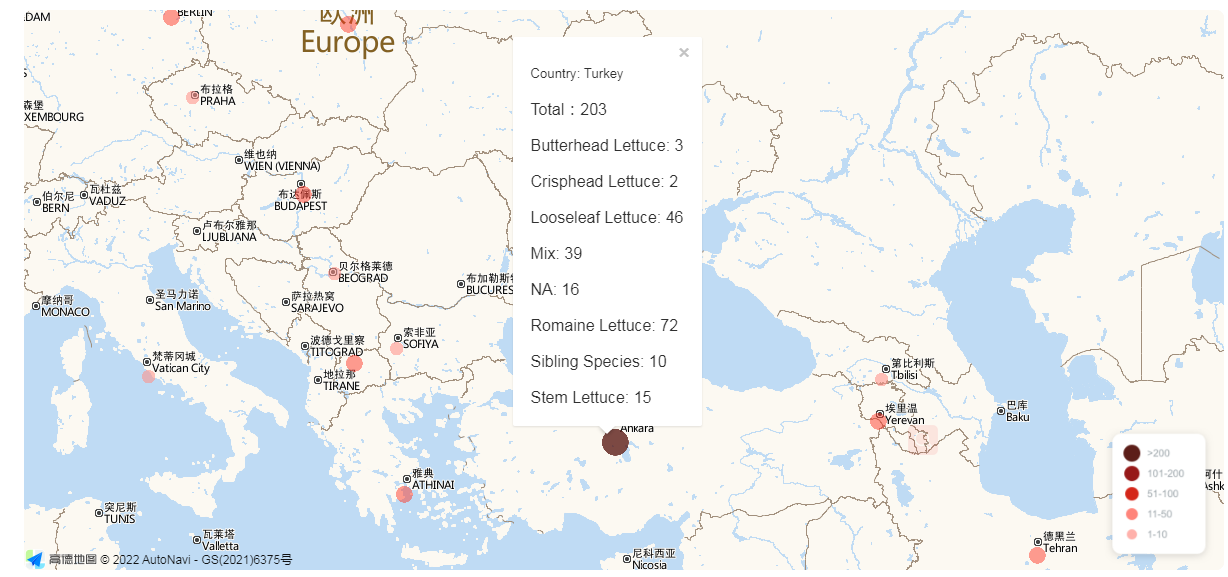
Interactive Germplasm Distribution Map Click the specific circle in the map to obtain the number of distinct types of lettuce sampled in this country.
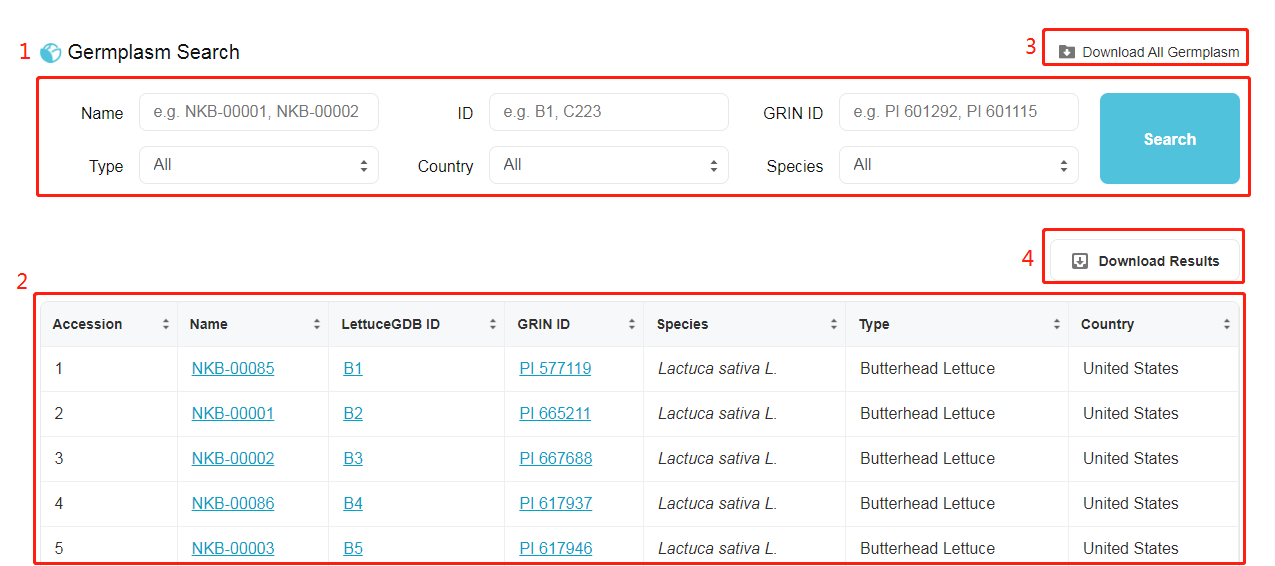
Germplasm Search Box 1. Search box: six arguments for searching and filtering germplasms by Name, ID, Type, Country or Species. Name, ID and GRIN ID are optional arguments. 2. Result box: showcase for filtered germplasms. 3. Download a TSV (Tab-separated values) file including all germplasm information. 4. Download a TSV file including filtered germplasm information.
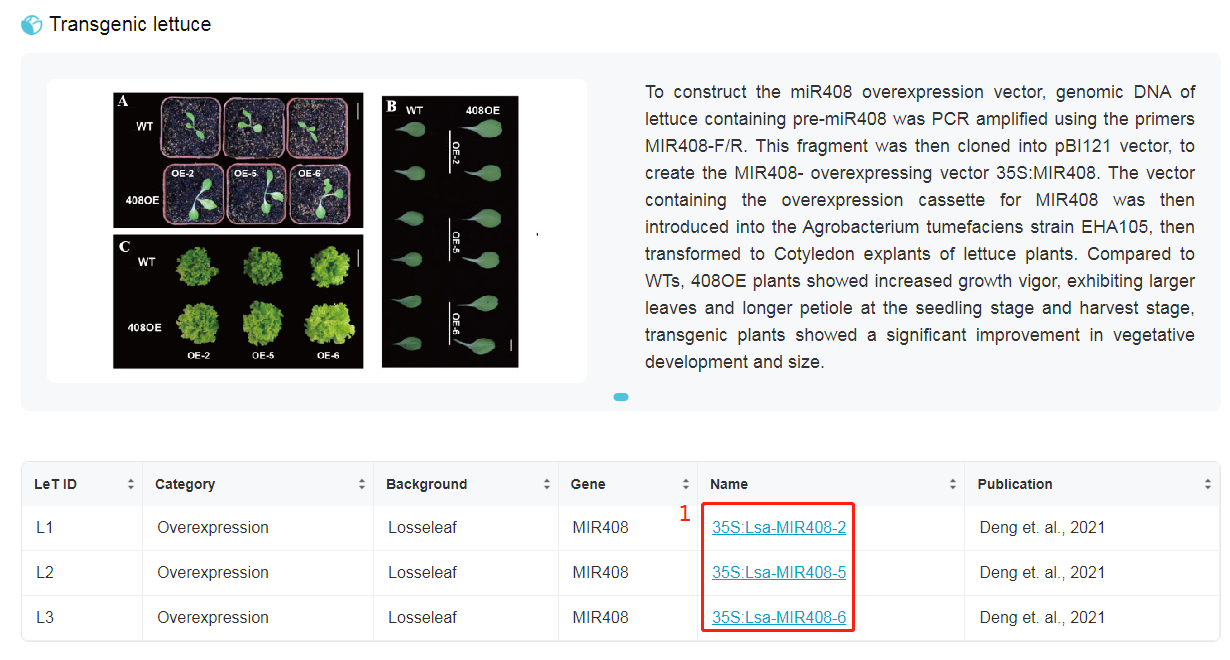
1. This table shows availably transgenic lettuces in LettuceGDB. Click on "Name" for detailed information of specific line. For more description of overexpressing MIR408 in lettuce, please read our published paper: Deng, Y., Qin, Y., Yang, P., Du, J., Kuang, Z., Zhao, Y., Wang, Y., Li, D., Wei, J., Guo, X., et al. (2021). Comprehensive Annotation and Functional Exploration of MicroRNAs in Lettuce. Frontiers in Plant Science 1210.3389/fpls.2021.781836

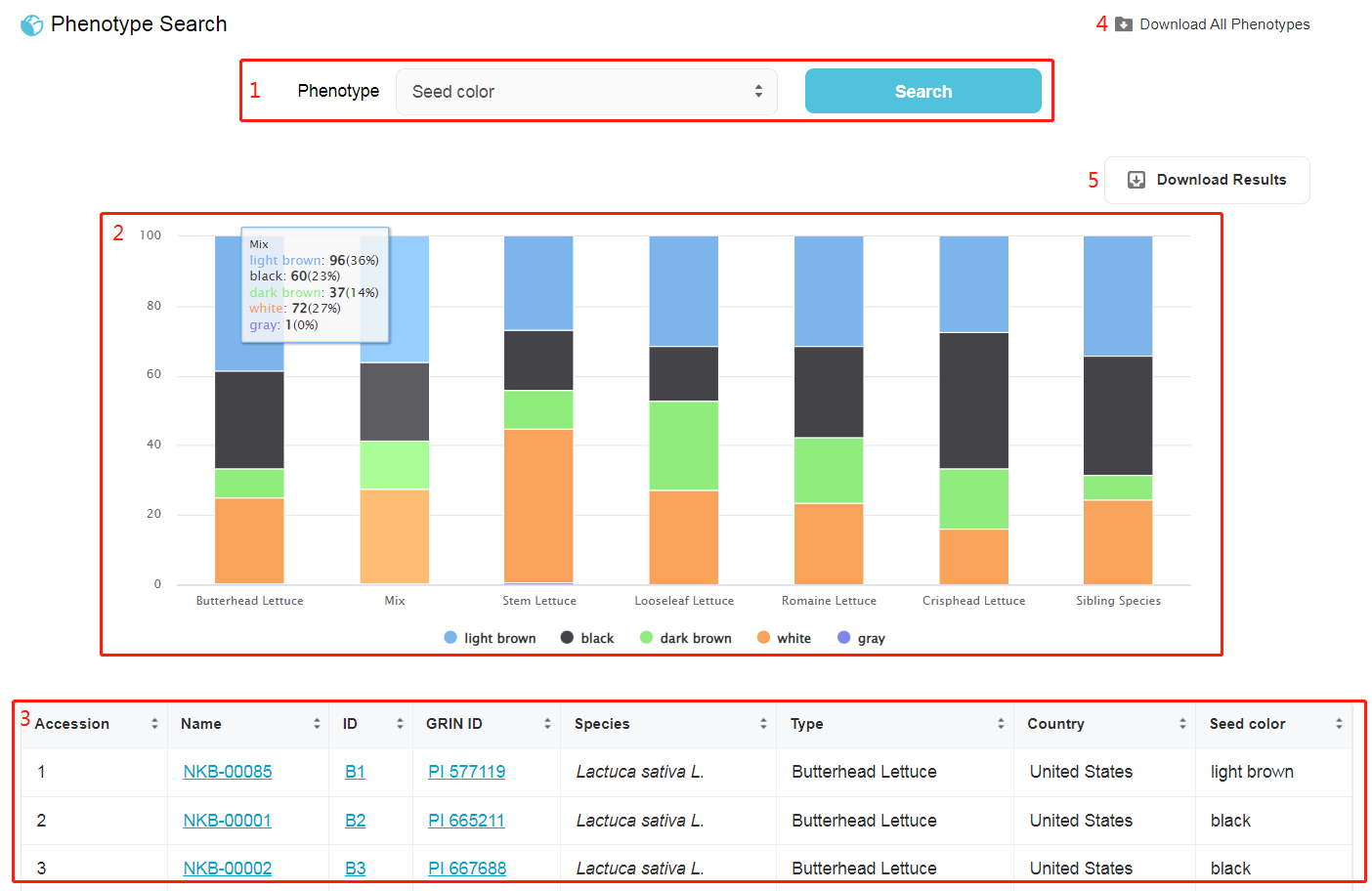
1. Selecting one phenotype, then showing the statistics of this phenotype in distinct types of lettuce. 2. Bar chart or box plot showing the statistics of the phenotype in distinct types of lettuce. 3. Result box: showcase for the manually phenotypical records in all germplasms. 4. Download a TSV (Tab-separated values) file including all phenotype information. 5. Download a TSV file including the selected phenotype information.
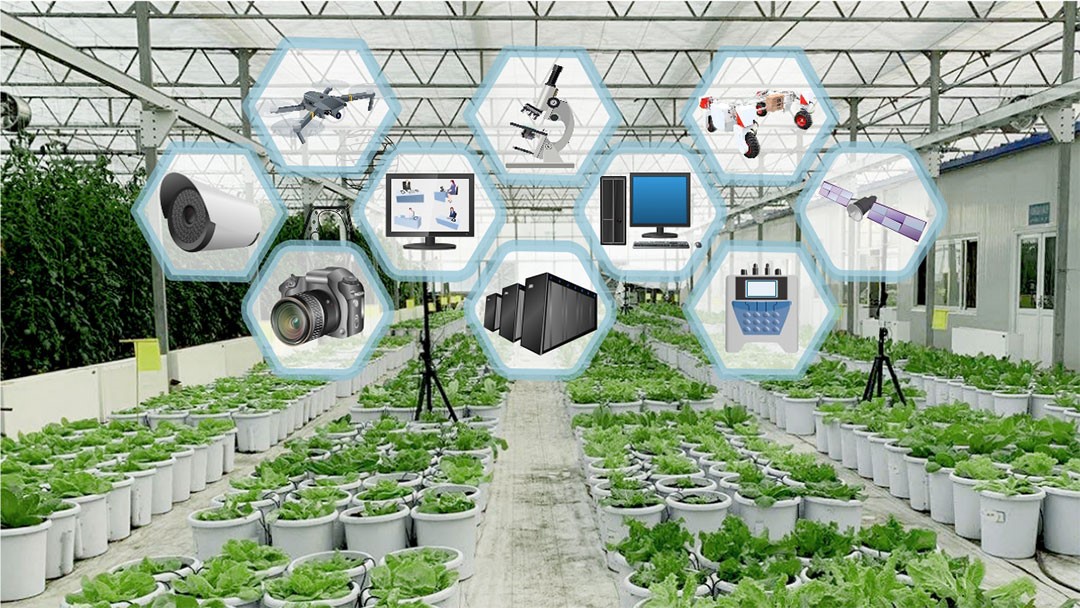

The high-throughput phenotyping platform was built in a terraced greenhouse at the Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences (BAAFS). The greenhouse structure was the conventional steeple terraced with a height of 6 m, a ceiling height of 6.5 m, a single span of 10.5 m, and a length of 45 m. Based on the ten load-bearing columns in the greenhouse, the north–south double-track beam (X) was installed at the height of 4.5 m above the ground, with a length of 40 m for each column, including two sets of synchronous motors, high-precision racks, synchronous belts, limit switches, and other components. The east–west beam frame (Y) was installed on the double-track beam and can control the overall motion in the X-axis direction. The beam frame also adopts the double-track beam as the basic structure, with an interval of 0.8 m. The rail trolley was mounted on it and can move stably in the Y-axis direction, including a set of synchronous motors, high-precision rack, synchronous belt limit switches, and other components.
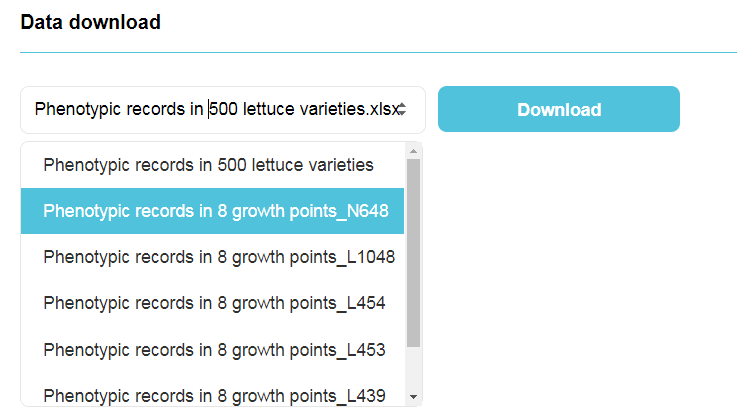
Users could download all available data in the bottom of this page. We will continually update new data recorded through high-throughput phenotyping platform.
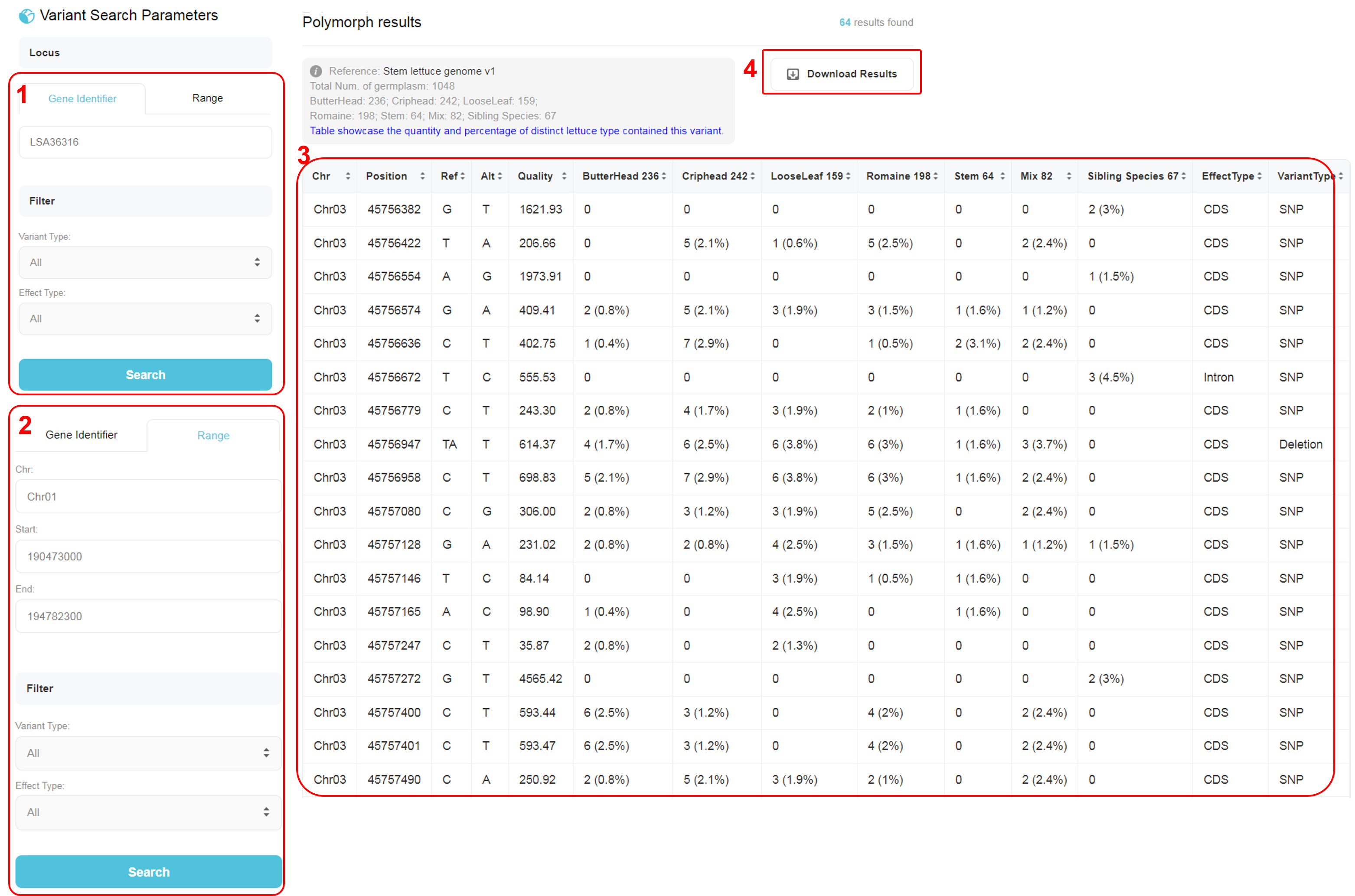
Two search modes are available in Genotype page, search by gene identifier or by range (of the chromosome). 1. Users could input a gene name, e.g. LSA36316, then select a variant type and effect type. The option “Variant Type” includes all, snp, insertion, deletion. The option “Effect Type” includes all, intergenic, promoter, intron, exon, 5’ UTR, 3’ UTR. 2. Users could input a range of genome, including chromosome (Chr), start position and end position. Then select a variant type and effect type as above. 3. The result table showcase the quantity and percentage of distinct lettuce type contained this variant. A complete file including all variants in 1,048 germplasms is available in Data page. 4. Download a TSV (Tab-separated values) file including the selected polymorph information.
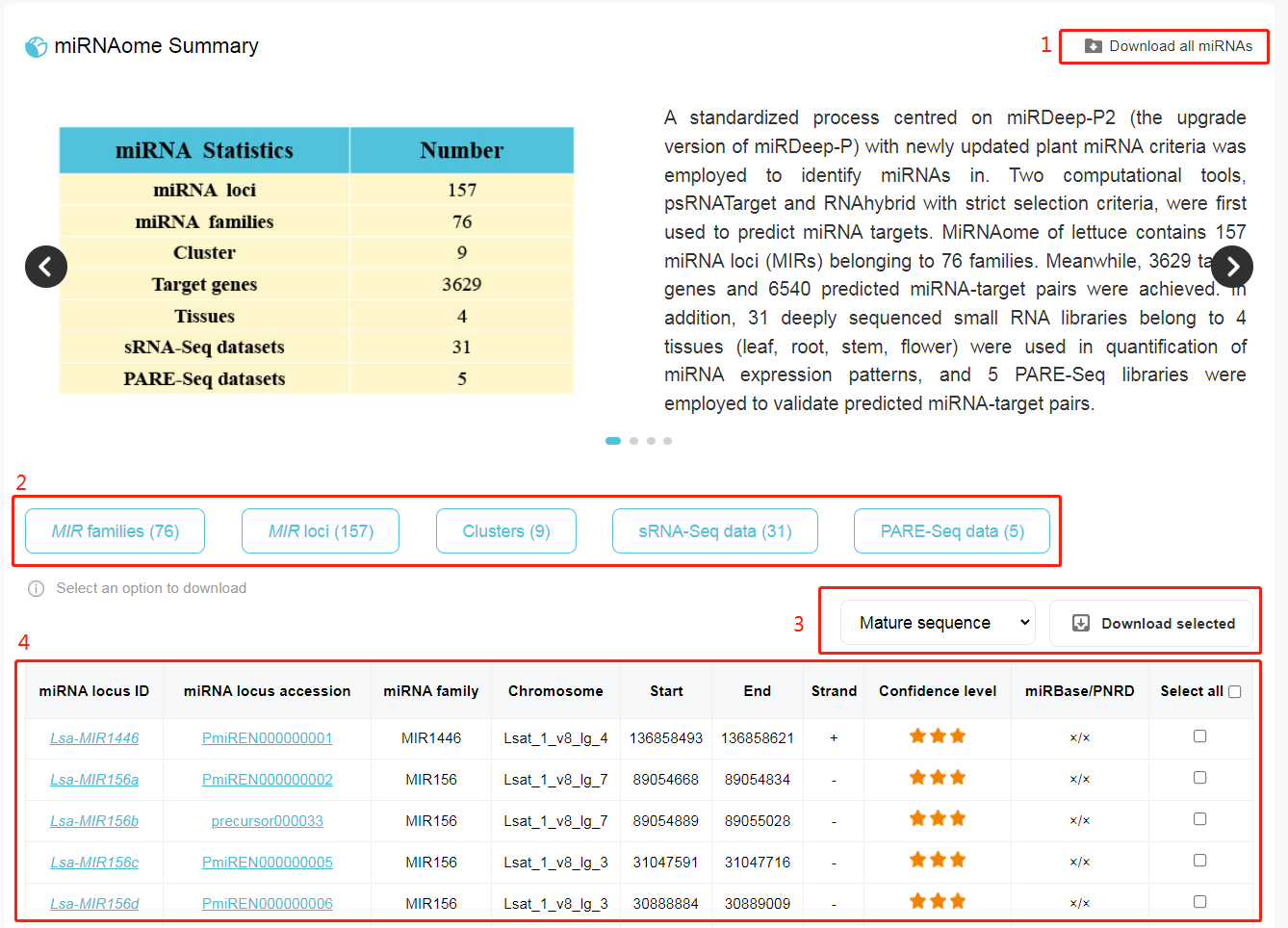
1. Download an Excel file including the basic information of all miRNAs identified in lettuce genome. 2. "MIR families" and "MIR loci" showcase a list of all miRNAs. "Clusters" exhibits 9 miRNA clusters (within 10 kb) in genome. "sRNA-Seq data" and "PARE-Seq data" show the metadata of 31 sRNA-seq libraries and 5 degradome libraries, respectively. 3. Selecting mature sequence, star sequence, stem-loop sequence or stem-loop +/-20 bp sequences to download. 4. The basic information of individual miRNAs. Clicking on miRNA locus ID or miRNA locus accession, go for the details of selected miRNA. Go to PmiREN for more details about miRNA page.
Presently, LettuceGDB contains 4,120 metabolites from 50 lettuce varieties belonging to six lettuce types, obtained through the liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method. Among the detectable compounds, 533 are annotated and are divided into ten groups, including alkaloids, amino acids and derivatives, flavonoids, lignans and coumarins, lipids, nucleotides and derivatives, organic acids, phenolic acids, terpenoids and others. LettuceGDB provides a retrieval system for a specific metabolite and a visual comparison among different types of lettuce.

1. Option box: n metabolites (compound) are grouped into n class I, n class II. Select a distinct metabolite using option box, then click "Search". 2. Box plot: Quantity of selected metabolite from 50 germplasms belonging to 6 type. 3. Result box: showcase for the mean values of selected metabolite in each type of lettuce. 4. Download a TSV (Tab-separated values) file including all metabolites information. 5. Download a TSV file including filtered metabolites information.
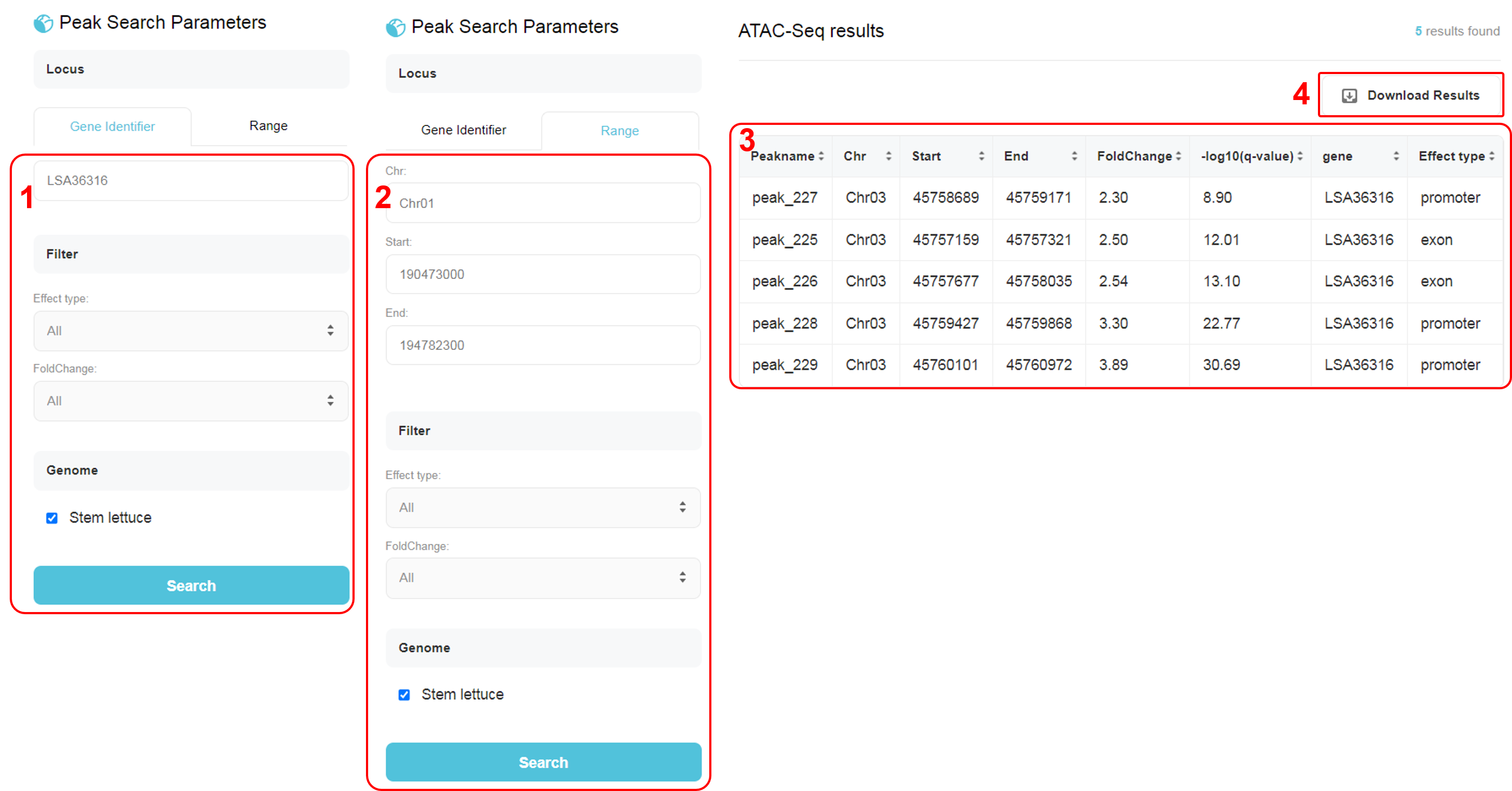
The interface and instruction of ATAC Seq page pretty resemble the Genotype page. Two search modes are also available in ATAC Seq page, search by gene identifier or by range (of the chromosome). 1. Users could input a gene name, e.g. LSA36316, then select a effect type and FoldChange. The option “Effect Type” includes all, promoter, exon, intron. The option “FoldChange” includes all, high, medium and low. 2. Users could input a range of genome, including chromosome (Chr), start position and end position. Then select a variant type and effect type as above. 3. The result table showcase the detailed information of significant peaks. 4. Download a TSV (Tab-separated values) file including the selected results of significant peaks.
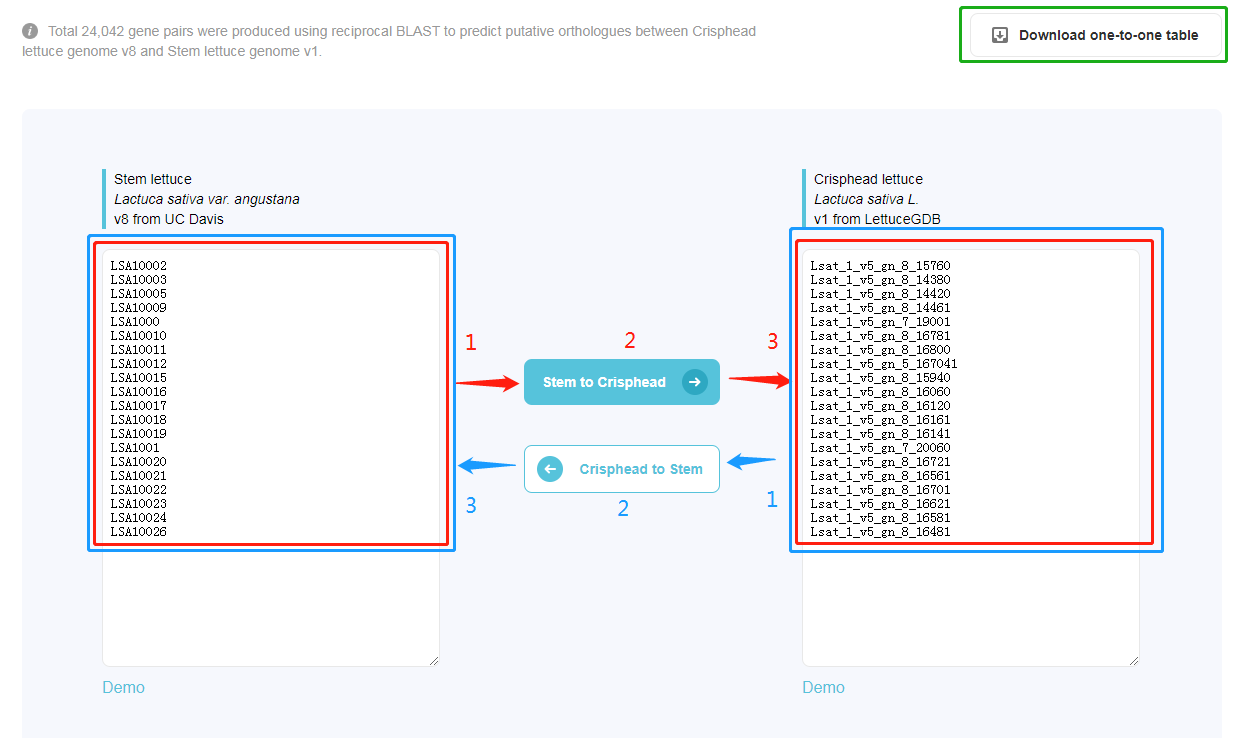
Total 24,042 gene pairs were produced using reciprocal BLAST to predict putative orthologues between Crisphead lettuce genome v8 and Stem lettuce genome v1.
The numbers in red indicate the steps of changing gene name from stem lettuce genome v1 to crisphead lettuce genome v8. The numbers in blue indicate the steps of changing gene name from crisphead lettuce genome v8 to stem lettuce genome v1. Green box: Download an Excel file "One-to-one gene id between Stem and Crisphead.xlsx", which contains all 24,042 gene pairs.

1. Searching gene by inputting a gene id. 2. Obtaining the sequences of queried gene, including genomic sequence, mRNA, CDS, protein and promoter (3,000 bp upstream of transcription start site). 3. An interactive mode of gene structure. Blue boxes represent exons. Black lines represent introns. An arrow indicates transcription direction. Double-stranded DNA sequences corresponding to horizontal scroll bar exhibit in the black box. 4. Bar chart showcase the expression (RPKM) of queried gene in 11 types of lettuce according to the RNA-seq data from Zhang et al.’s paper.
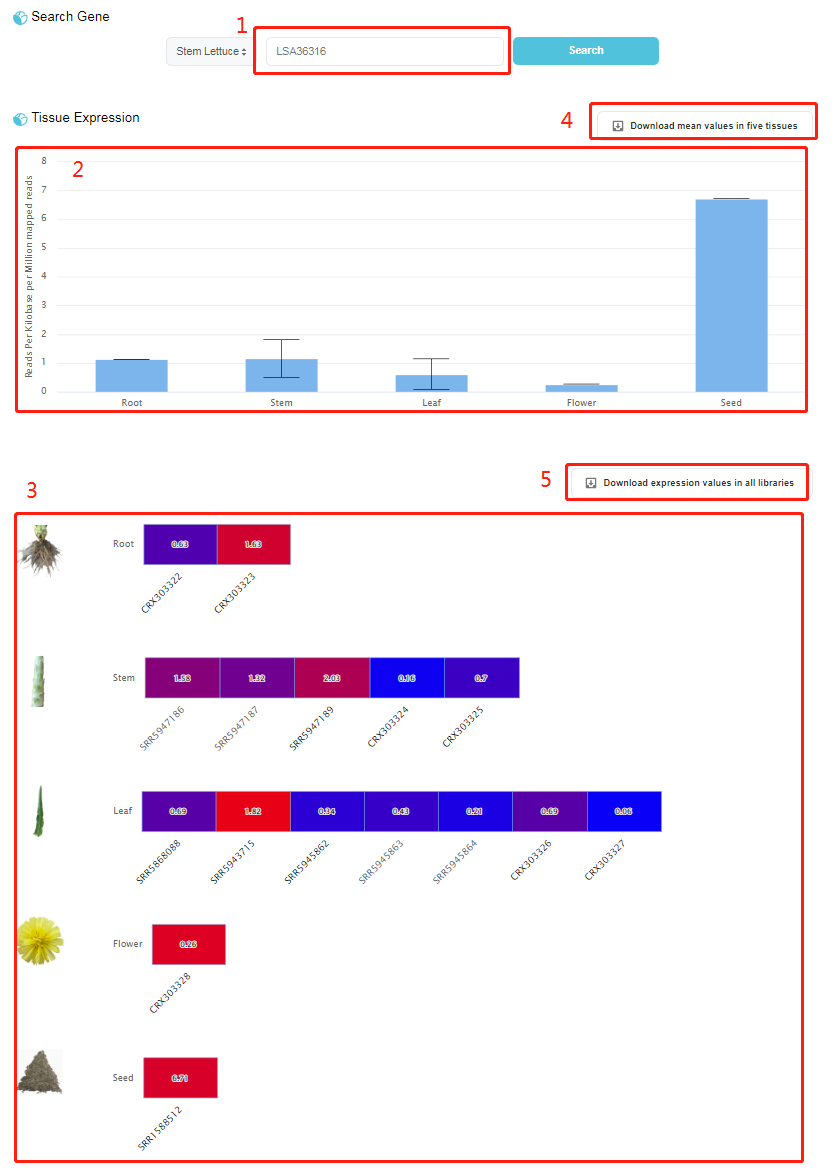
1. Search box: inputting a gene name 2. Bar chart showing the average expression level of queried gene in root, stem, leaf, flower and seed. 3. Heat map showing the expression level of queried gene in specific RNA-seq libraries. 4. Download an Excel file, "Mean expression values in five tissues.xlsx", which contains the mean expression values of all genes. 5. Download an Excel file, "Expression values in all libraries.xlsx", which contains the expression values of all genes in all RNA-seq libraries.
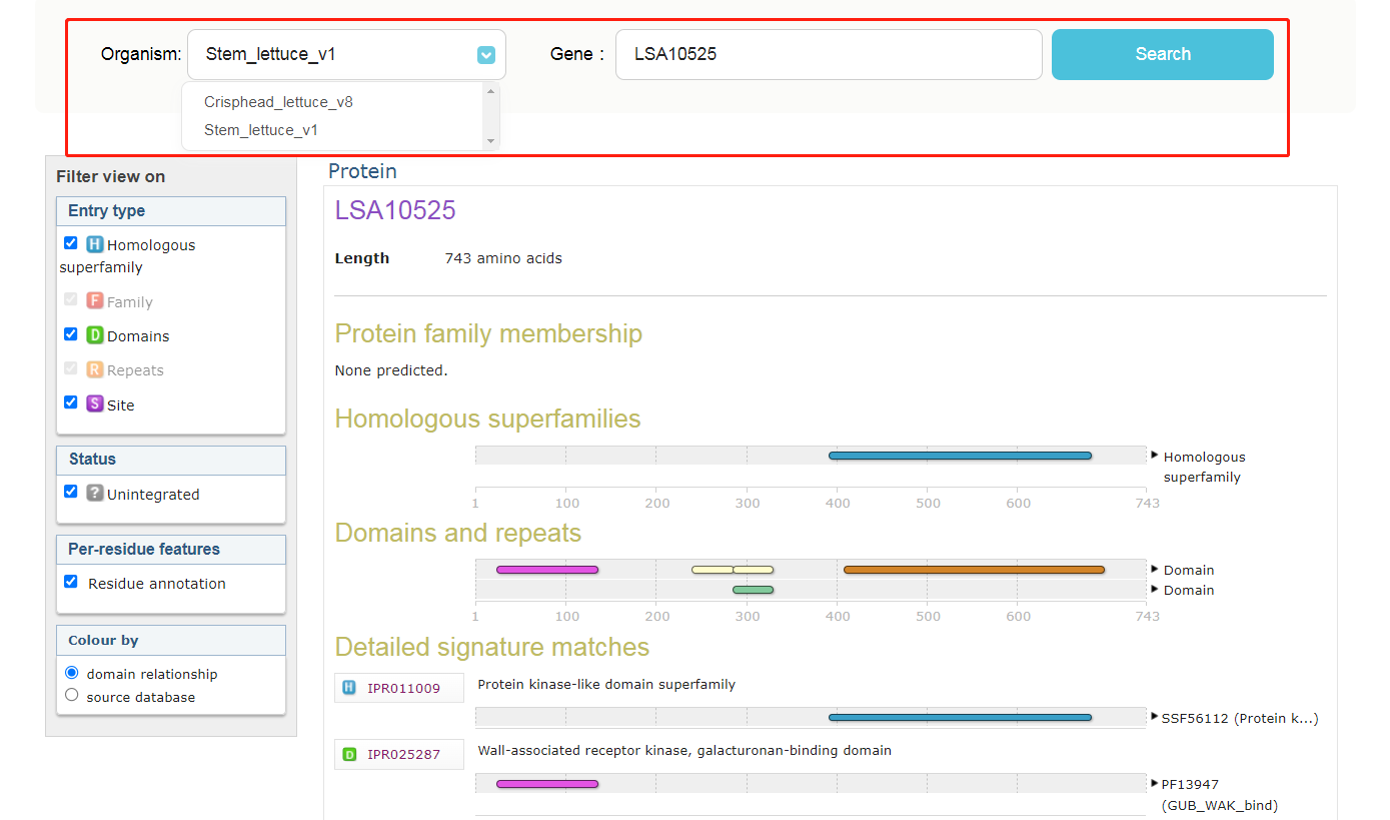
InterproScan was implemented to annotate gene from both crisphead lettuce v8 and stem lettuce v1. Users just need to input a gene id, then click on button "Search".
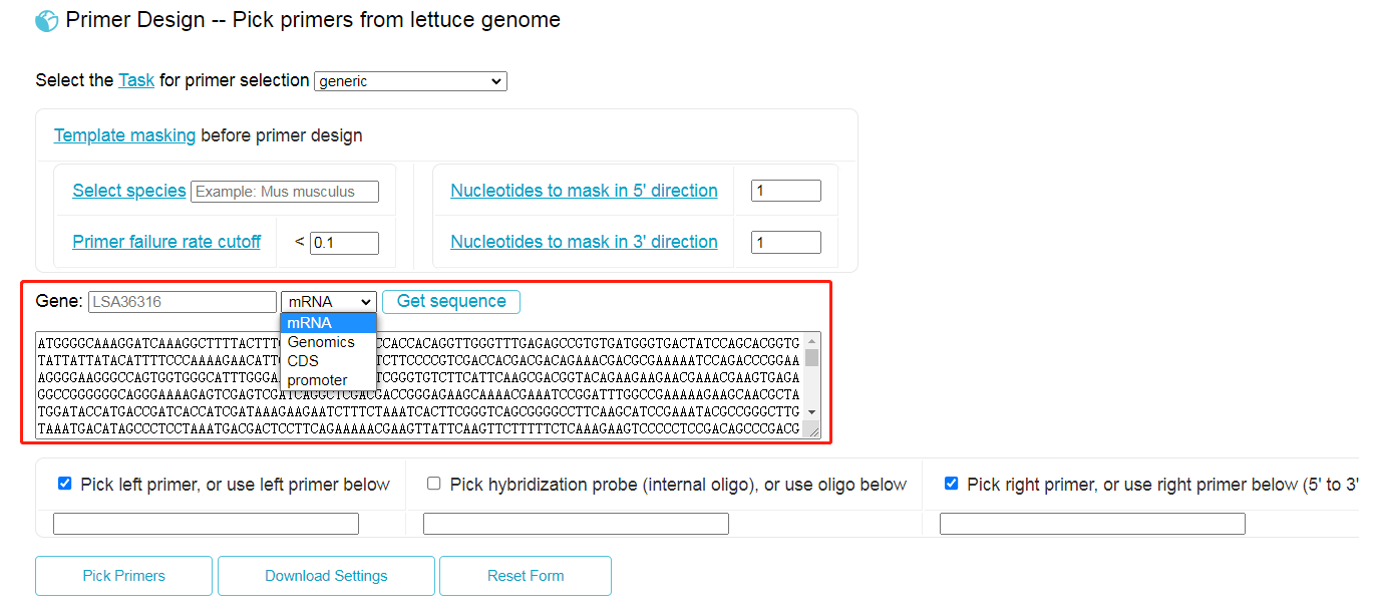
Primer3 is a widely used program for designing PCR primers (PCR = "Polymerase Chain Reaction"). PCR is an essential and ubiquitous tool in genetics and molecular biology. Primer3 can also design hybridization probes and sequencing primers. PCR is used for many different goals. Consequently, primer3 has many different input parameters that you control and that tell primer3 exactly what characteristics make good primers for your goals. LettuceGDB integrates a modified version of primer3, by which users only need to input a gene id before selecting mRNA, Genomic, CDS or promoter in the pull-down menu (see red box). Then, clicking on the button “Get sequence”, the sequences will be filled in automatically.
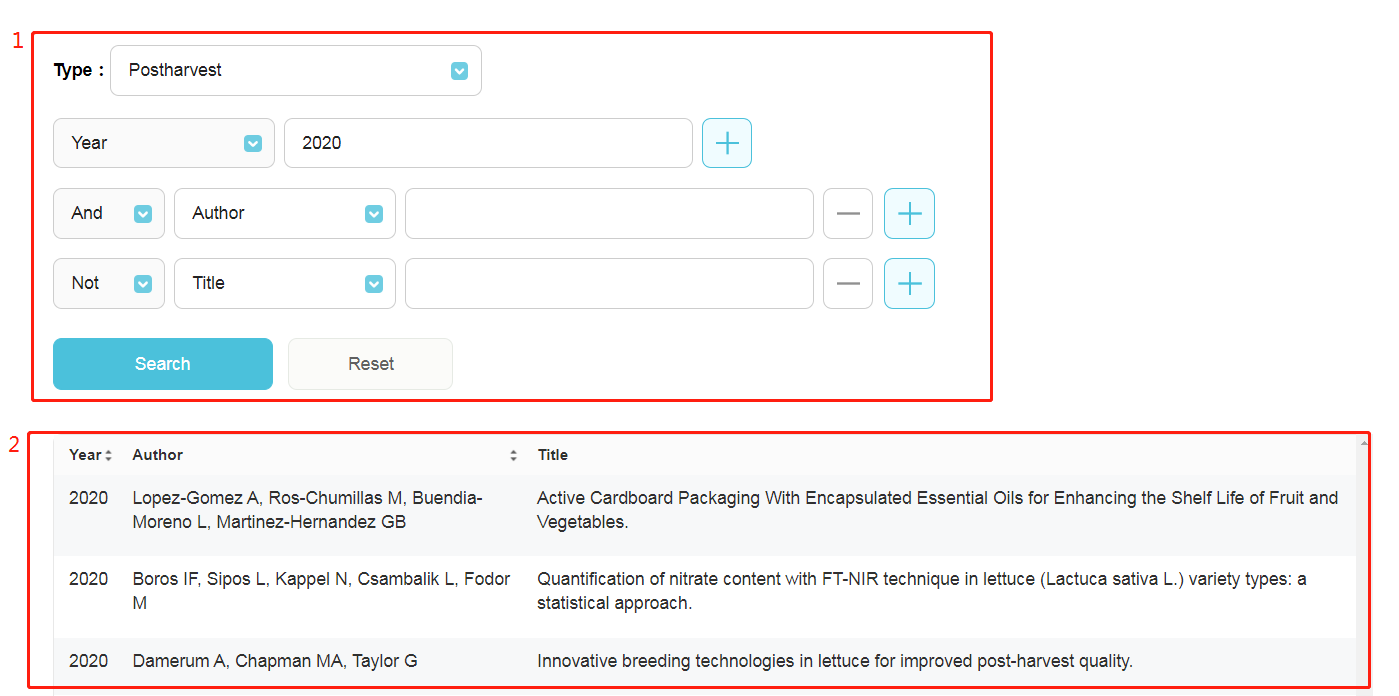
1. Searching box for literature regarding to lettuce: Total 2,597 publications were manually grouped into 50 types. Six options, including year, author, title, journal, keyword, abstract, are used to filter publications. 2. Result table: Clicking on a title, then jumping to the full text of this paper.