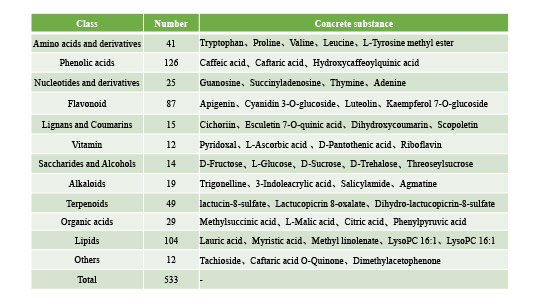
Considering the genetic relationship, geographical origin and phenotypic differences, we selected 50 most representative samples of different types of lettuce. These materials were planted in the field and leaves were taken 35 days after transplanting, with at least three plants from each material. Metabolites were obtained based on the liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method. Among the detectable compounds, 533 of them are annotated, which are divided into ten groups, including alkaloids, amino acids and derivatives, flavonoids, lignans and coumarins, lipids, nucleotides and derivatives, organic acids, phenolic acids, terpenoids and others. Among them, metabolites belonging to phenolic acids have been identified the most.
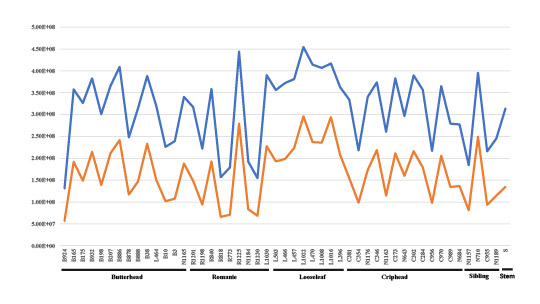
Alkaloids are a type of nitrogen-containing alkaline organic compounds that exist in nature (mainly plants), and have alkali-like properties. Indole alkaloids are derived from tryptophan, which have a large number and complex structure, and most of them have significant biological activity. Indole has been reported to be used more in anti-hypertensive, anti-proliferative, anti-viral, anti-tumor, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial and other therapeutic fields. As the picture shows that there are obvious differences in the content of the same metabolite (3-Indoleacrylic acid and 1-Methoxy-indole-3-acetamide) in different varieties, which lays the foundation for the quality breeding of lettuce in the next step.
| Compound | 中文名 | Butterhead | Romanine | Looseleaf | Crisphead | Stem | Sibling species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|