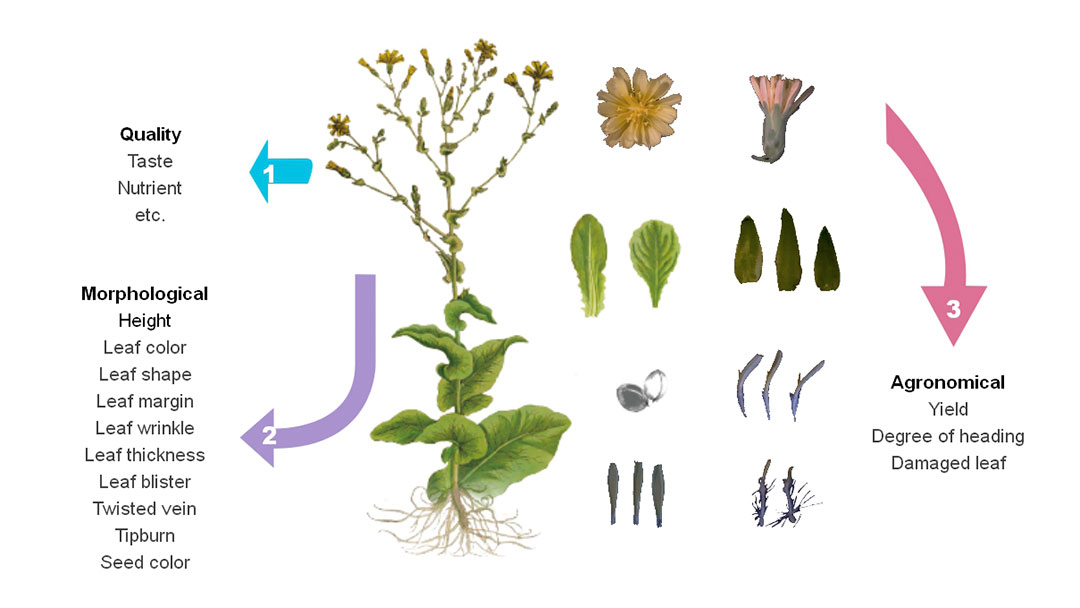
Over the past three years, we manually recorded 13 traits of the 1,313 germplasms at five locations. Tens of thousands of records and photos have been made and taken. For instance, the leaves of different cultivars are colorful, mainly in the green and red color spectrums, with some variegated varieties. There are also a few varieties with yellow, gold or blue-teal leaves. Based on the observations, we divided leaf color into five categories, light green, green, dark green, light red, red. Another example is the seed color, we grouped them into five categories, light brown, dark brown, black, white, gray. Considering the variations of growth conditions, when we treated these phenotypic records, a normalization of each trait was employed.

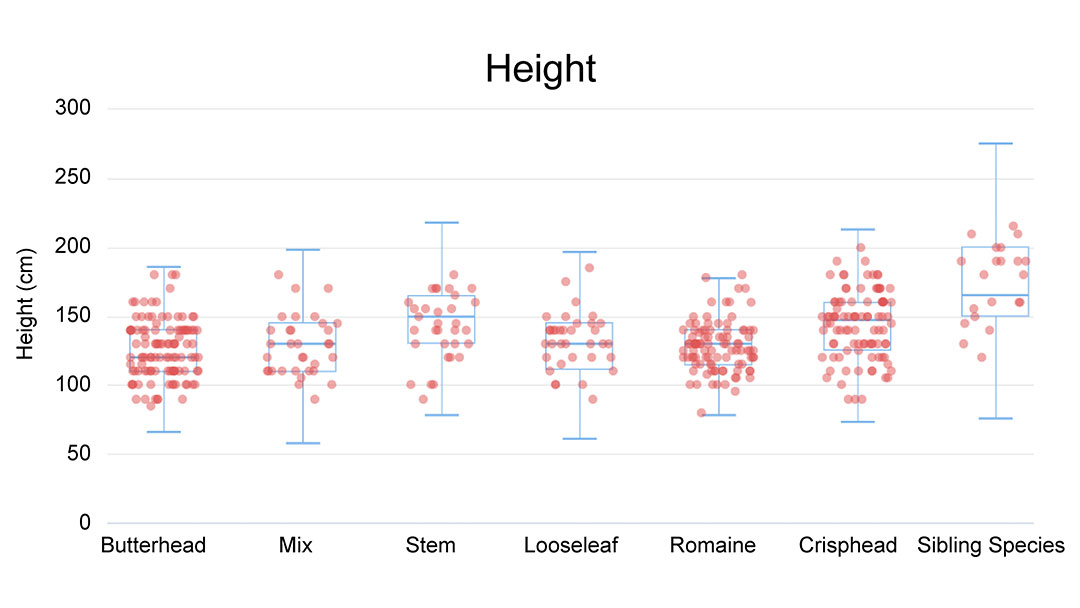
Plant height is one of the most basic indexes in plant morphological investigation. It is defined as the distance from the base of plant to the top of main stem, i.e. the growing point of the main stem. The box scatter chart height chart on the left shows the distribution of plant heights in seven types (Butterhead, Crisphead, Stem, Looseleaf, Romaine, Mix, Sibling Species) lettuce. Among them, the plant height of Sibling species is generally higher than that of cultivated species. Beside of plant height, bolting time also showed using box scatter plot. In addition, other 11 phenotypes are showed using percentage stacked bar chart, including tipbum, leaf color, seed coat color, leaf shape, leaf margin, leaf winkle, leaf thickness, thickness, twisted vein, leaf blister, degree of heading.