On the end year of 2018, we initialized the project of sequencing the cultivar, stem lettuce.
Stem lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. angustana), also called Chinese lettuce, is a cultivar of lettuce grown primarily for its thick stem or its leaves. It is used as a vegetable and is especially popular in China and east Asian, where the stem is interchangeably called qingsun (Chinese: 青笋) or wosun (Chinese: 莴笋).
To produce a high-quality stem lettuce reference genome, we generated a de novo assembly of stem lettuce ‘Yanling1’ (YL1) composed of 280 assembled scaffolds and arranged into 9 pseudomolecules, which represent the 9 chromosomes of lettuce. This assembly resulted from a combination of short (Illumina) and long sequencing reads (PacBio), along with scaffolding based on optical maps (BioNano) and chromosome conformation capture (HiC) (Table 1). This chromosome-scale assembly was complemented by a detailed de novo annotation of genes based on RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) data, TE annotation and small RNA alignments.
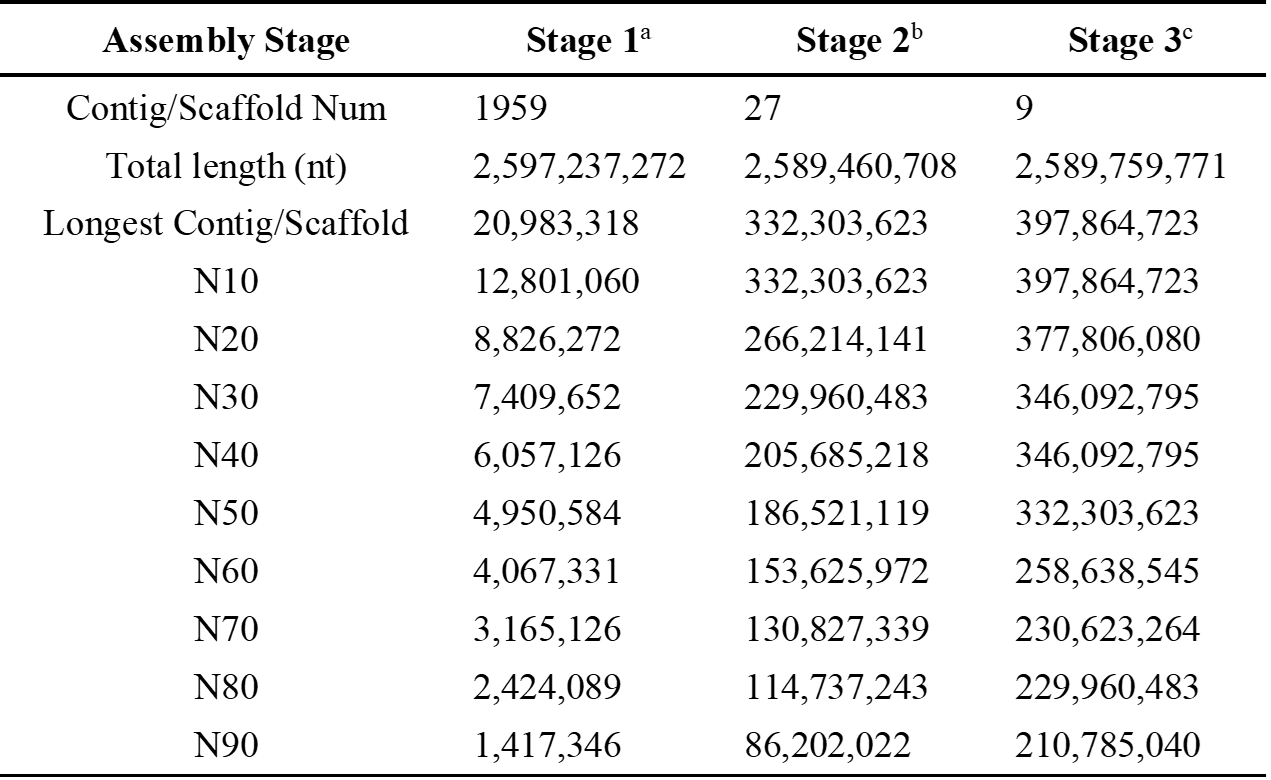
Table 1. Assembly of stem lettuce. Note: Stage 1a: the assembly generated only by PacBio data; Stage 2b: the assembly generated by PacBio and Bionano data; Stage 3c: the assembly generated by PacBio, Bionano and HiC data.